Mastering Control Panel Design: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to the world of precision and innovation, where control panel design is an art and a science. In this comprehensive guide brought to you by MIS Controls, a distinguished woman-owned business and a proud member of the Women’s Business Enterprise National Council (WBENC), we’ll take you on a journey from the basics to the intricate details of mastering control panel design. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced engineer, this guide is your roadmap to crafting control panels that set the industry standard.
Chapter 1: The Basics of Control Panel Design
1.1 Understanding Components
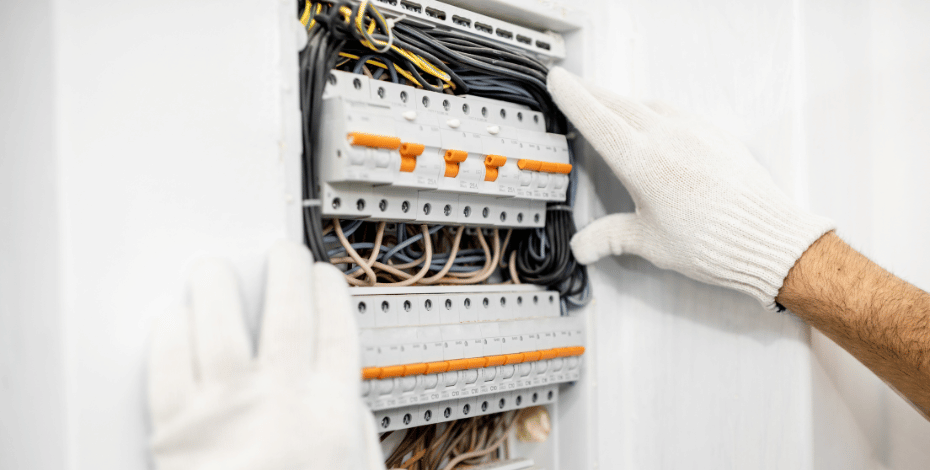
Control panel design starts with a deep understanding of the components involved. From enclosures to power supplies and controllers, MIS Controls emphasizes the importance of choosing quality components that align with the specific requirements of the application.
- Enclosures: The protective shield for delicate components, available in various materials for durability and environmental resistance.
- Power Supplies: Providing the necessary electrical energy for the system to function efficiently.
- Controllers: Acting as the brains of the control panel, interpreting signals and directing the operation of connected devices.
1.2 Wiring Essentials
Wiring is the intricate network that ties the components together. At MIS Controls, precise wiring is considered an art form. Beginners are introduced to the basics of wiring, understanding color codes, and the significance of organized cable management.
- Color Coding: Adhering to industry-standard color codes ensures consistency and simplifies troubleshooting.
- Cable Management: Organized cables not only enhance aesthetics but also contribute to ease of maintenance and troubleshooting.
1.3 Safety Considerations
MIS Controls places safety at the forefront of design. Beginner designers are introduced to safety standards such as UL508A, emphasizing the importance of enclosures, circuit protection, and proper grounding.
- Enclosure Safety: Preventing accidental contact with live components and shielding against environmental factors.
- Circuit Protection: Incorporating circuit breakers and fuses to safeguard against electrical faults and overloads.
Chapter 2: Intermediate Control Panel Design
2.1 Advanced Wiring Techniques
As designers progress, they delve into advanced wiring techniques, mastering the art of creating intricate yet organized wiring systems. MIS Controls emphasizes the importance of maintaining signal integrity and minimizing electrical noise.
- Twisted Pair Wiring: Minimizing electromagnetic interference by pairing wires carrying signals in close proximity.
- Shielding Techniques: Using shielded cables to protect sensitive signals from external interference.
2.2 Human-Machine Interface (HMI) Integration
The intermediate stage introduces designers to the importance of user interaction. Control panels become more than just functional; they become user-friendly interfaces, allowing operators to monitor and control systems seamlessly.
- Switches and Indicators: Strategically placed for easy access and quick troubleshooting.
- Touchscreen HMIs: Incorporating advanced interfaces for enhanced user experience and control flexibility.
2.3 Integrating PLCs for Automation
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) become integral components at this stage. Designers learn to program PLCs for precise control, automation, and flexibility in adapting to different scenarios.
- Precision Control: Programming PLCs for intricate and precise control of connected devices.
- Flexibility in Automation: Adapting PLC programs for various applications and scenarios.
Chapter 3: Advanced Control Panel Design
3.1 IoT Integration
In the advanced stage, designers explore the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), enhancing control panels with connectivity and data analytics capabilities.
- Remote Monitoring: Enabling real-time monitoring and diagnostics from anywhere.
- Predictive Maintenance: Anticipating and addressing potential issues before they occur.
3.2 Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
MIS Controls prioritizes sustainable practices, and advanced designers are introduced to the concept of energy-efficient control panel design.
- Energy-Efficient Components: Selecting components that contribute to overall system efficiency.
- Green Manufacturing Practices: Incorporating eco-friendly materials and processes in control panel assembly.
Mastering control panel design is an evolving journey that encompasses both foundational principles and advanced techniques. At MIS Controls, this journey is a commitment to precision, safety, and innovation. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced designer, this comprehensive guide provides insights into the art and science behind crafting control panels that define excellence in the industry. As a woman-owned business at the forefront of control panel manufacturing, MIS Controls continues to inspire the next generation of designers to push the boundaries of what is possible in control panel design.
For more detail on this topic, please refer to the Mastering Control Panel Design eBook for free download today!
